Transformer Formula Sheet - Each inductor loop is in. Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Equivalent resistance of transformer windings:
A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: Each inductor loop is in.
Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: Each inductor loop is in. Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Equivalent resistance of transformer windings:
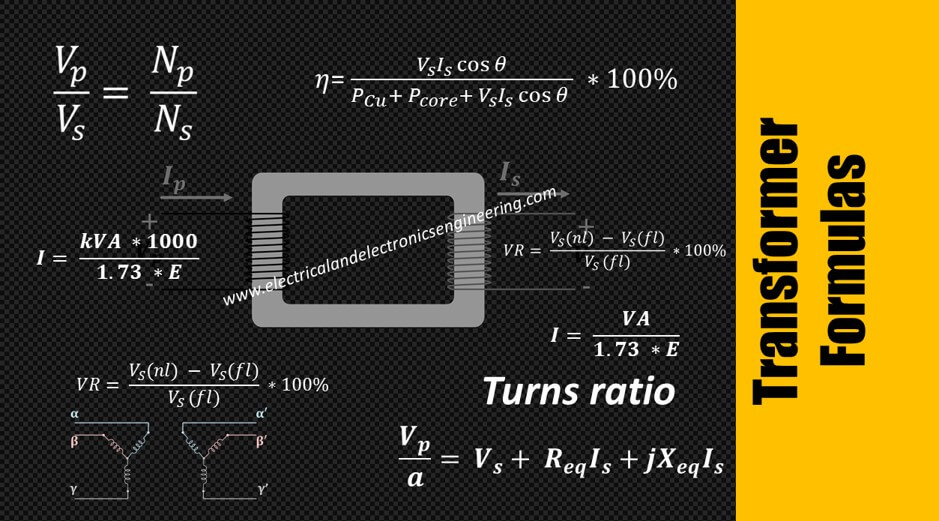
Top 10 Transformer Formulas Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Each inductor loop is in. A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors:
Formula Sheet 2 Transformer Where N1 are the voltage and number of
\[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of.
Current transformer (CT) saturation calculator EEP
A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Each inductor loop is in. Equivalent resistance of.
Transformer Calculation Sheet
Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}}.
Transformer Formula Sheet
A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors:
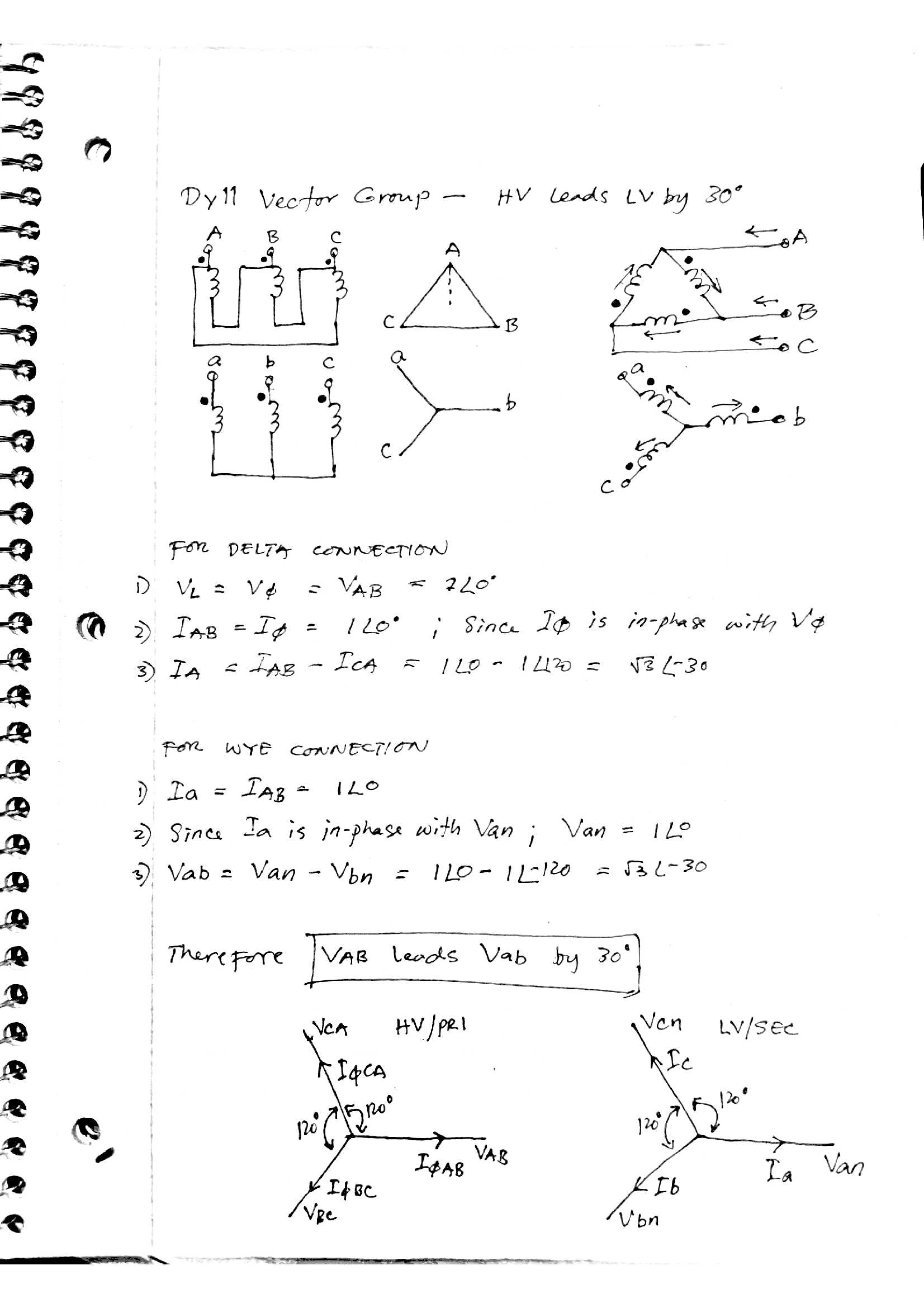
Transformer Vector Groups Basic Concepts Part 1 Electrical
Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: Each inductor loop is in. Emf induced in primary &.
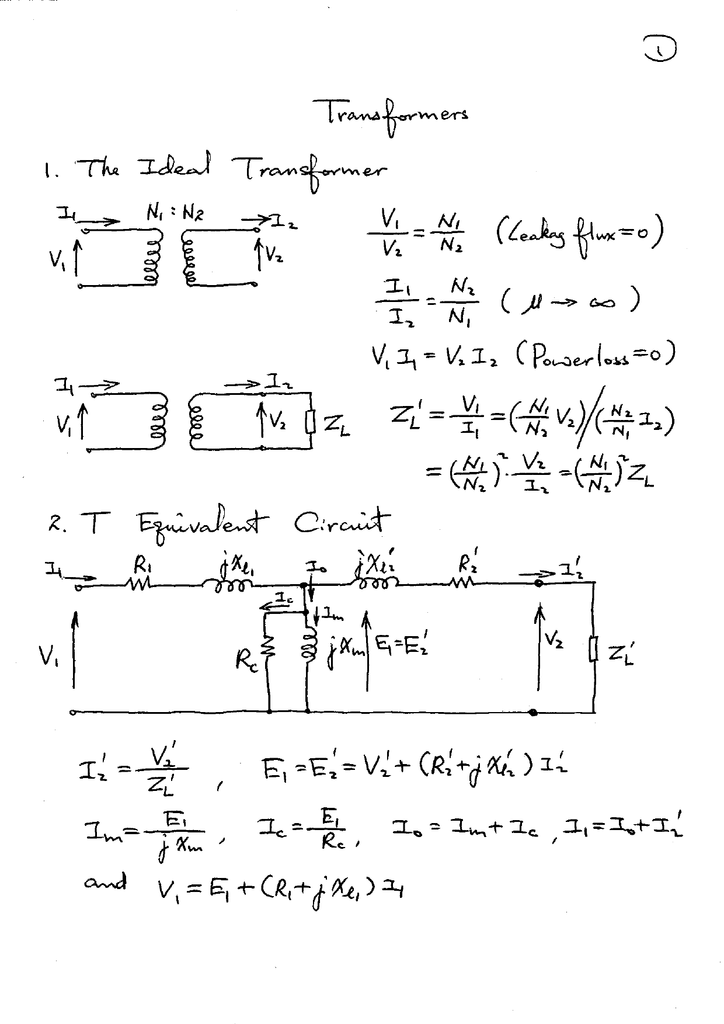
Transformer Circuit and Equation YouTube
Each inductor loop is in. A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of.
Simplifying the transformer equation YouTube
A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil.
Pin on Electrical
Emf induced in primary & secondary windings: Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil. \[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] =.
Power And Distribution Transformers Sizing Calculations Part Eight
\[v_{s} = \frac{n_{s}}{n_{p}} \times v_{p}\] where, \[n_{p}\] = number of turns in the primary \[n_{s}\] = number of. Each inductor loop is in. Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Equivalent resistance of transformer windings:
Emf Induced In Primary & Secondary Windings:
Web figure 1 as seen in figure 1, the transformer has two inductors: A source (or primary) inductor (ls) and a load (or secondary) inductor (ll). Equivalent resistance of transformer windings: Each inductor loop is in.
\[V_{S} = \Frac{N_{S}}{N_{P}} \Times V_{P}\] Where, \[N_{P}\] = Number Of Turns In The Primary \[N_{S}\] = Number Of.
Web as the transformer is basically a linear device, a ratio now exists between the number of turns of the primary coil divided by the number of turns of the secondary coil.