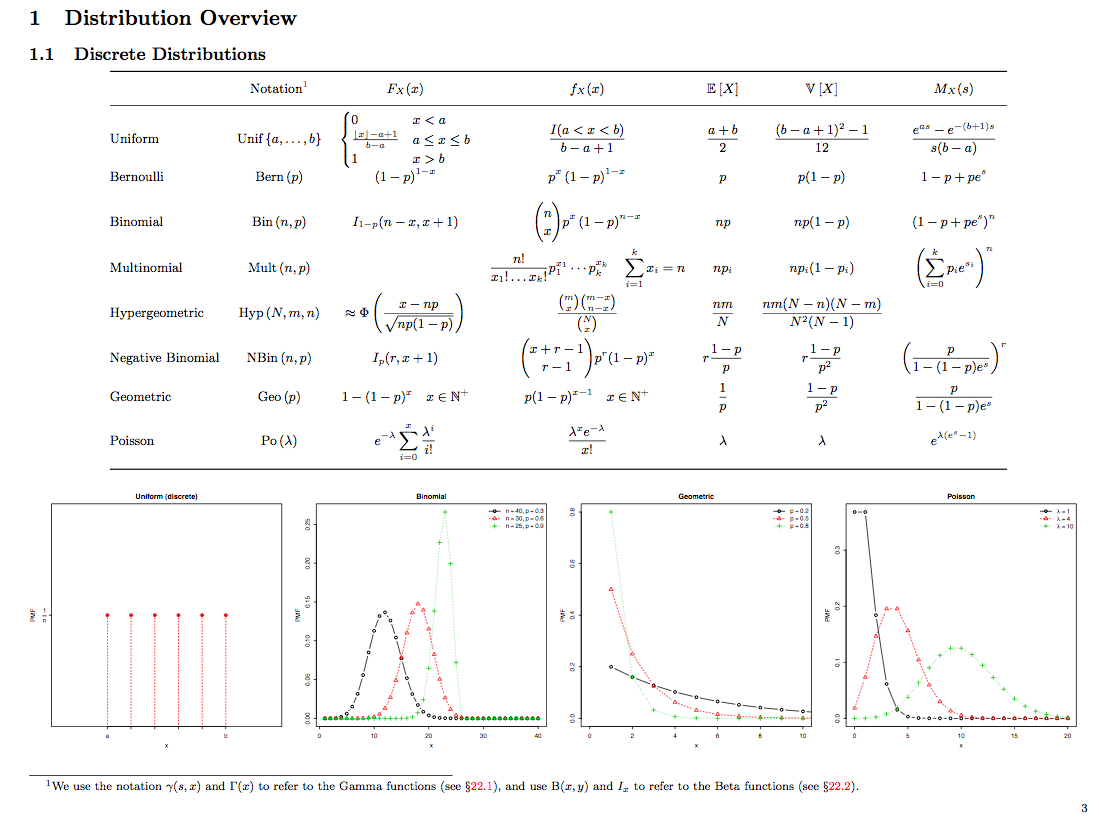
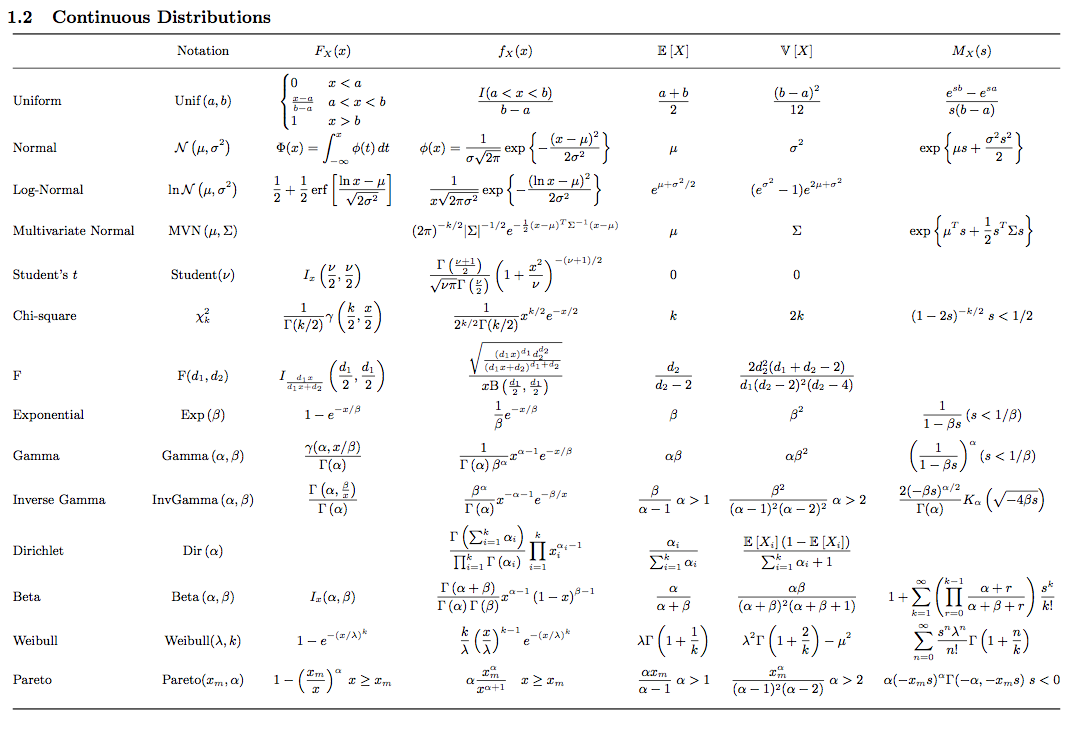
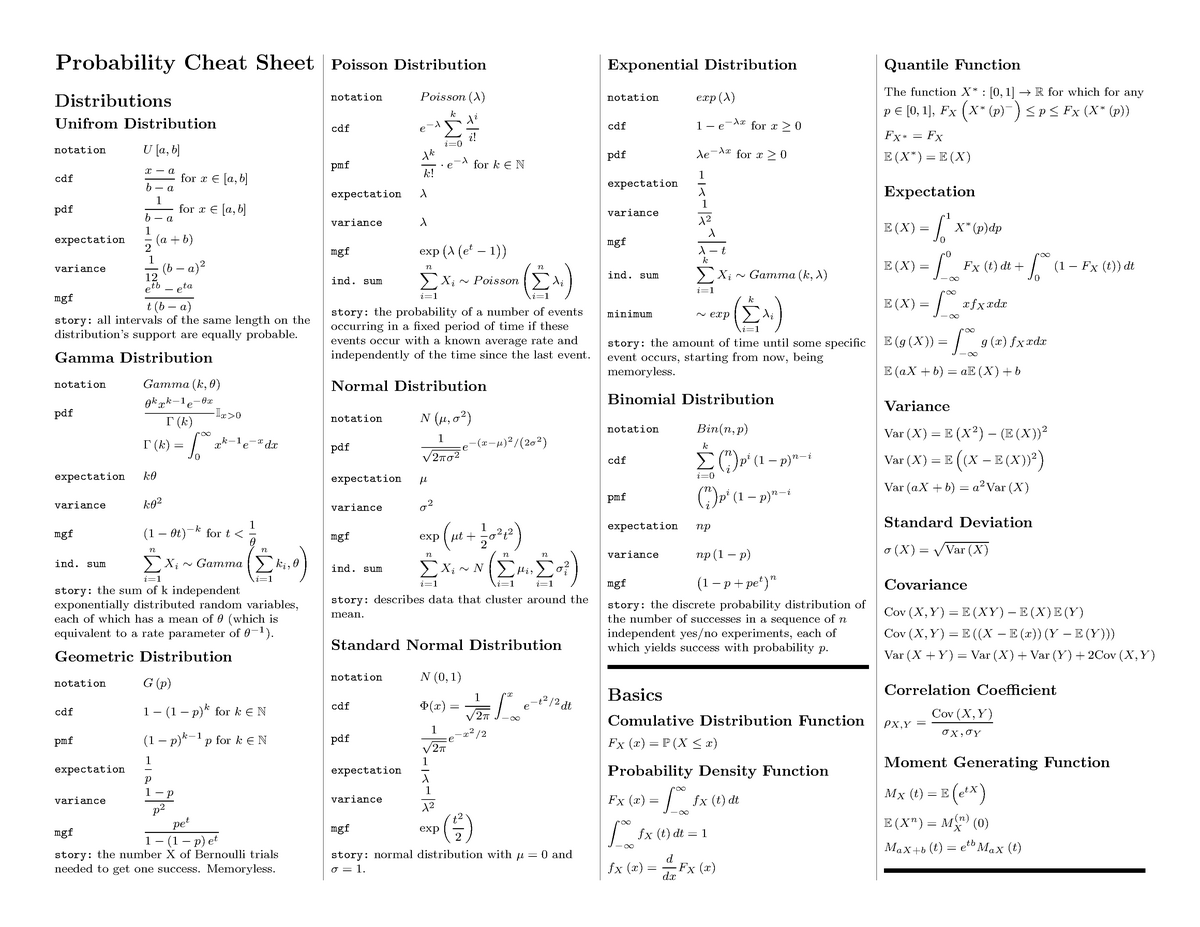
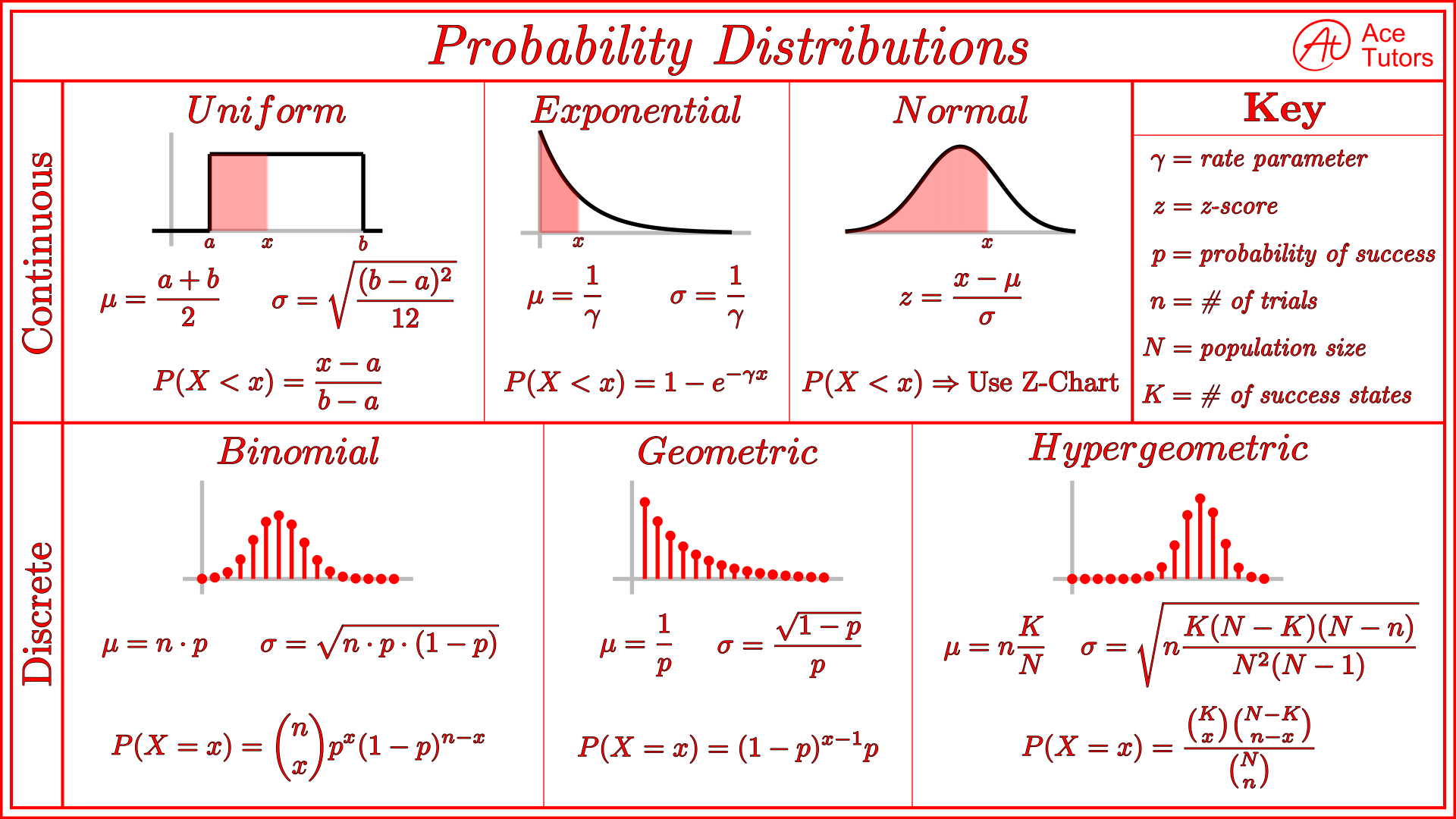
Distribution Cheat Sheet - { there are no true model parameters. Web a (v) a < b p 1. A > b means a is bigger than b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web certain probability distribution (gaussian for example). B means a is less than b. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. Web continuous probability distributions.
2 probability the chance of a certain event. Web a (v) a < b p 1. Web continuous probability distributions. A > b means a is bigger than b. Web certain probability distribution (gaussian for example). Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. { there are no true model parameters. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: Material based on joe blitzstein's.
For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: Web continuous probability distributions. When you work with continuous probability distributions, the functions can take many forms. These include continuous uniform, exponential, normal, standard. Web a (v) a < b p 1. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event. A > b means a is bigger than b. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$.
math notation cheat sheet Web cheatsheet bashooka es6
Web continuous probability distributions. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: B means a is less than b. Material based on joe blitzstein's. Web a (v) a < b p 1.
Matthias Vallentin Probability and Statistics Cheat Sheet
{ the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web continuous probability distributions. Web certain probability distribution (gaussian for example). Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. A b means that a is less than or the same as b.
Chapter 7 Sampling and Sampling Distributions Cheat Sheet from
Web a (v) a < b p 1. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: 2 probability the chance of a certain event. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. These include continuous uniform, exponential, normal, standard.
Get my art printed on awesome products. Support me at Redbubble
2 probability the chance of a certain event. A > b means a is bigger than b. B means a is less than b. Web certain probability distribution (gaussian for example). Web a (v) a < b p 1.
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet Probability Cheat Sheet
B means a is less than b. These include continuous uniform, exponential, normal, standard. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality:
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet Calculus Ace Tutors Blog
{ the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. B means a is less than b. A > b means a is bigger than b. When you work with continuous probability distributions, the functions can take many forms.
the table shows different types of numbers and their corresponding
{ there are no true model parameters. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. A > b means a is bigger than b. When you work with continuous probability distributions, the functions can take many forms. Web a (v) a < b p 1.
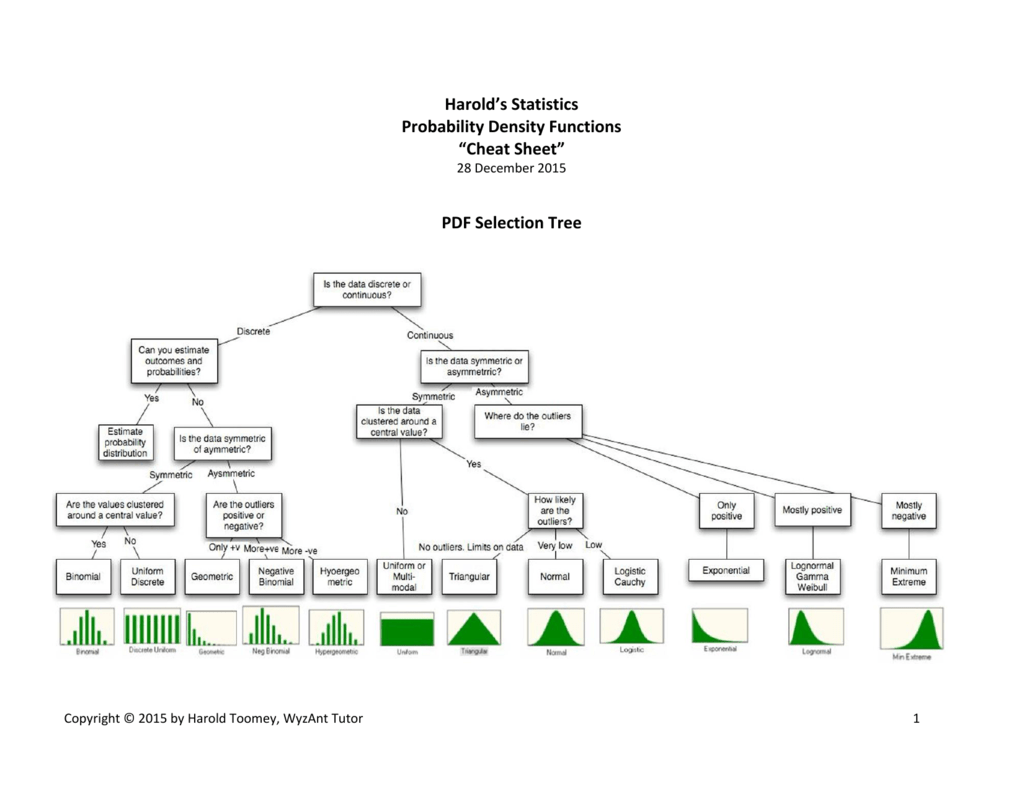
Harold's Statistics PDFs Cheat Sheet
These include continuous uniform, exponential, normal, standard. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. A > b means a is bigger than b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a;
GitHub wzchen/probability_cheatsheet A comprehensive 10page
Web a (v) a < b p 1. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; A > b means a is bigger than b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality:
GitHub wzchen/probability_cheatsheet A comprehensive 10page
A b means that a is less than or the same as b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: Web continuous probability distributions. { there are no true model parameters. These include continuous uniform, exponential, normal, standard.
Web Continuous Probability Distributions.
These include continuous uniform, exponential, normal, standard. Material based on joe blitzstein's. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; { there are no true model parameters.
When You Work With Continuous Probability Distributions, The Functions Can Take Many Forms.
B means a is less than b. Web certain probability distribution (gaussian for example). A > b means a is bigger than b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality:
2 Probability The Chance Of A Certain Event.
Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. Web a (v) a < b p 1. A b means that a is less than or the same as b.