Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest - Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic.
Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic.
Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic.
(PDF) Dihydrocapsaicininduced Hypothermia after Asphyxial Cardiac
Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have.
Cardiopulmonary Arrest Anesthesia Key
Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic.
Cardiac Arrest Induced by Asphyxia Versus Ventricular Fibrillation
Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have.
ECLS treatment increased the plasma levels of proinflammatory and
Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole.
(PDF) Different Respiratory Rates during Resuscitation in a Pediatric
Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole.
(PDF) Neurologic after Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest in a Juvenile
Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic.
Asphyxial cardiac arrest (ACA) and CPR rat model. (A) Timeline of ACA
Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic.
(PDF) DCycloserine 24 and 48 Hours after Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest has
Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole.
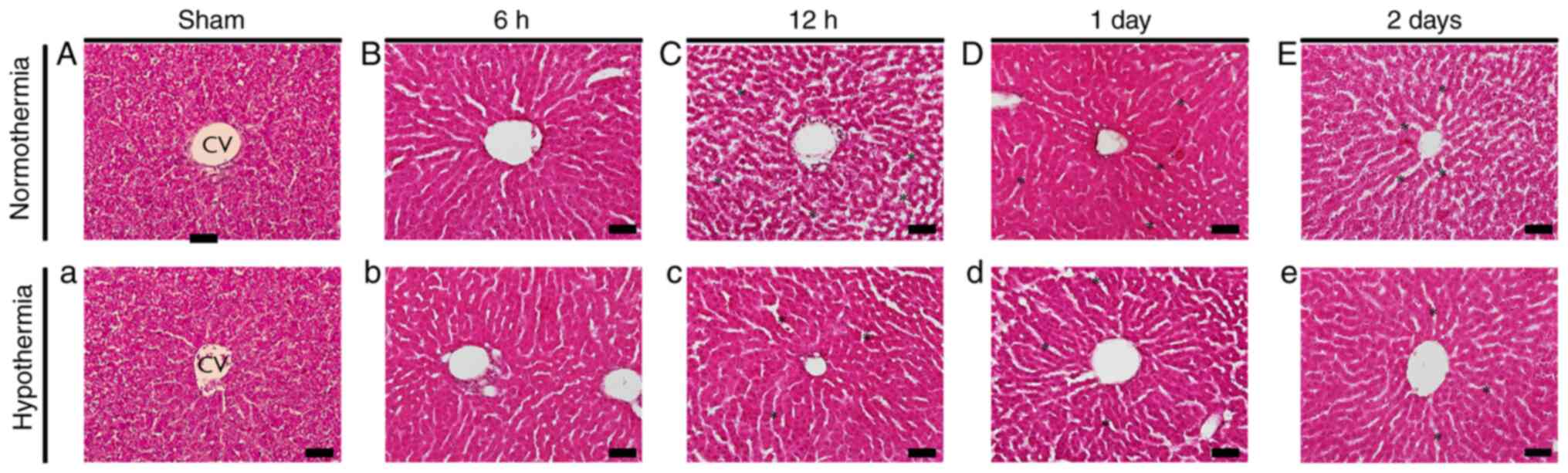
Effects of hypothermia on inflammatory cytokine expression in rat liver
Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole.
Abstract 70 The Difference of Cardiac Mitochondrial Damage Between
Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole. Asphyxial cardiac arrest differs significantly from dysrhythmic cardiac arrest with regard to pathophysiologic. Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have.
Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Differs Significantly From Dysrhythmic Cardiac Arrest With Regard To Pathophysiologic.
Web asphyxia is also the mechanism of cardiac arrest in most children, although about 5% to 15% have. Web the majority of all asphytic cardiac arrests begin with pea and progress to asystole.